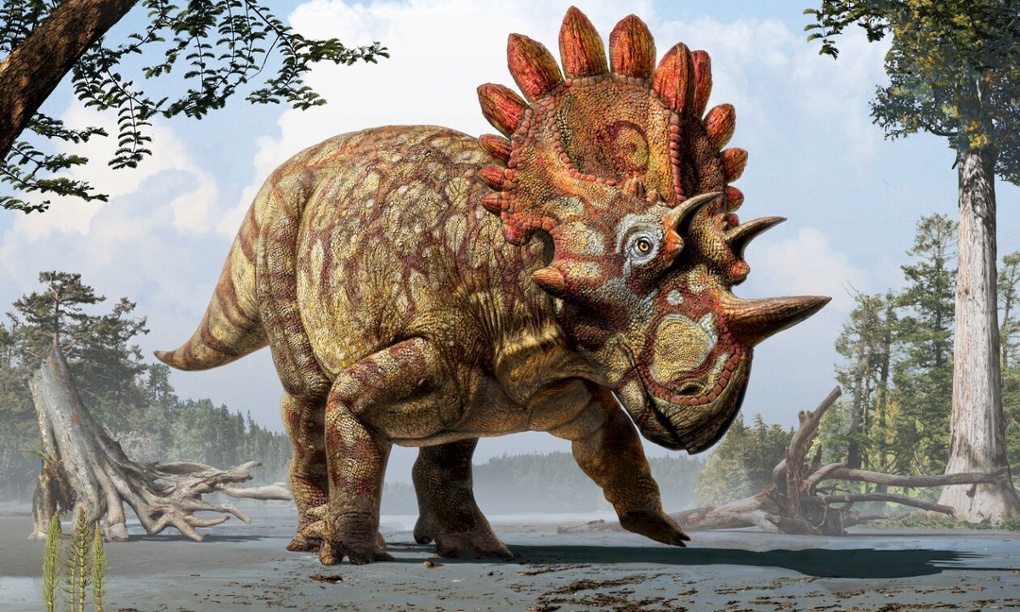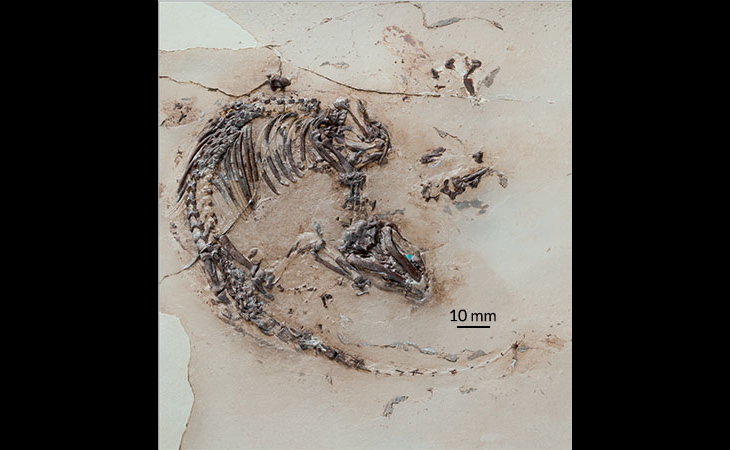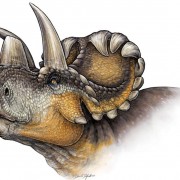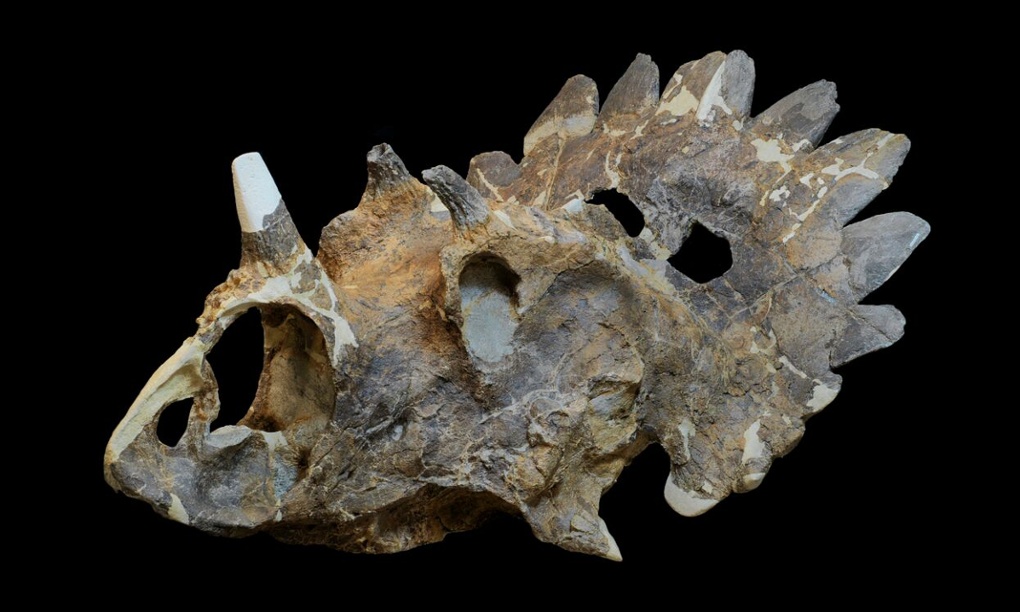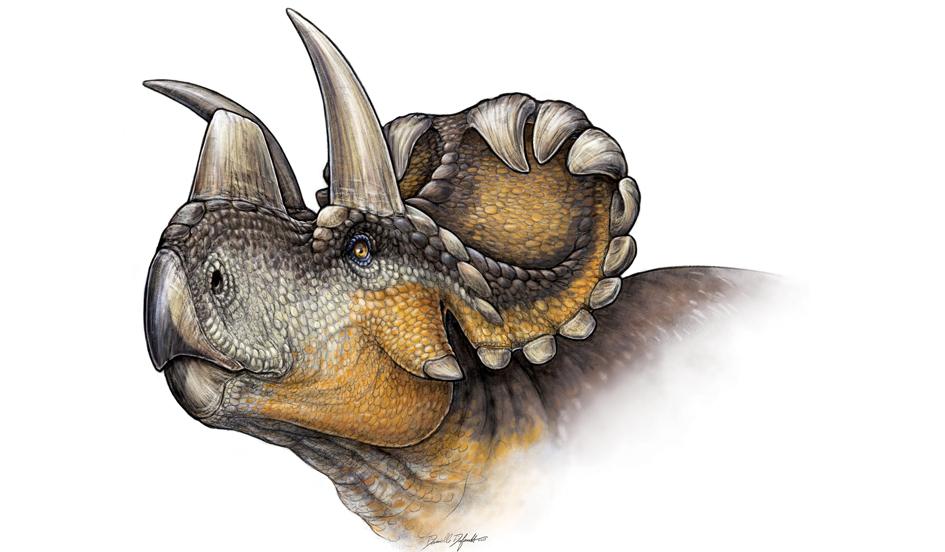
A team of Canadian scientists announced that bones found in 2010 are from a new dinosaur they named Wendiceratops. DANIELLE DUFAULT/ROYAL ONTARIO MUSEUM
Scientists have discovered one of the oldest horned dinosaurs, a one-ton behemoth that had spikes above its eyes, on its nose and covering almost its entire neck.
The new dinosaur, named Wendiceratops pinhornensis, is described from over 200 bones representing the remains of four specimens from the group of large-bodied dinosaurs known as the Ceratopsidea. It lived about 79 million years ago, making it 13 million years older than its famous cousin Triceratops and one of the few specimens of this group from the late Campanian period, stretching from 90 million to 77 million years ago, found in North America.
It was found at a site in southern Alberta five years ago by Wendy Sloboda, a famous fossil hunter who has made hundreds of discoveries over the past three decades.
“She came across the site in 2010 and it actually had parts of the skull weathering out on the surface,” said Royal Ontario Museum’s David Evans, who co-authored a study on the find in PLOS One with the Cleveland Museum of Natural History’s Michael Ryan. Sloboda was part of the research team.
“When she brought them to us, we were very excited because the parts she brought back were part of the frill which has that characteristic ornamentation,” he said of the back of a dinosaur’s head. “Right away, we knew we likely had a new species of dinosaur. The first season we starting digging in 2011, we found more of the frill. At that point, we were certain. So, the race was on to collect as much as we could.”
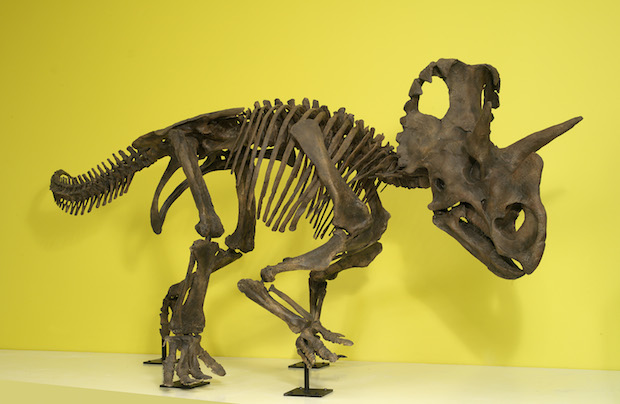

The skeleton is a 3-D printed model of a Wendiceratops based on the adult bones found at a Canadian site in 2010. BRIAN BOYLE
Evans said Wendiceratops, which means “Wendy’s horned-face” (it was named for Sloboda) could be the first of this dinosaur group to have a horn – or more accurately horns.
“The wide frill of Wendiceratops is ringed by numerous curled horns, the nose had a large, upright horn, and it’s likely there were horns over the eyes too,” he said. “The number of gnarly frill projections and horns makes it one of the most striking horned dinosaurs ever found.”
It featured a series of forward-curling hook-like horns that adorned the margin of the wide, shield-like frill that projects from the back of the Wendiceratops’ skull. The nasal bone, although represented by fragmentary specimens, likely supported a “prominent upright nose horn.”
“There is a huge diversity in horned dinosaurs. They are mostly differentiated from each other by the shapes, sizes and direction of the horns on their face and on their neck shield,” Evans said. “This particular one is really extravagant for any horned dinosaur. It has this array of large, forward-facing horns that surround the entire of margin of the neck shield. It would have looked like a halo of drooping horns all the way around the back of the skull.”
The nose horns, which scientists once thought were mostly for defense, are believed to have been used to attract mates and establish the dinosaurs rank in its herd – much like modern animals like antelope or water buffaloes use their horns.
It was probably even made from the same material as some modern animal horns, keratin.
The fact these fossils show horned dinosaurs go much further back than previously believed, Evans said, “helps us understand the early evolution of skull ornamentation in an iconic group of dinosaurs characterized by their horned faces.”
“We don’t actually have a good idea exactly what the nose horn looked like in terms of its overall shape,” he said, adding they had three partial specimens but no complete nose horn.

Field crew systematically excavating the
“But what we can say is that it looks transitional between its ancestors that lacked a horn and later horned dinosaurs that had very prominent, very tall conical horns over their nose,” he said. “This skull ornamentation devolved very rapidly in the diversification of horned dinosaurs which suggests that mating signals were key in the early radiation of the group.”
Andrew Farke, a paleontologist with Raymond M. Alf Museum of Paleontology who last year discovered Aquilops, the oldest horned dinosaur in North America that lived as far back as 145 million years ago, said the latest discovery offers fresh insight into the dinosaur horn.
Horned dinosaurs were commonplace during the Cretaceous period but died out when the Earth was struck by what scientists believe was an asteroid. They then emerged again with the Ceratopsidea group that included Wendiceratops.
“Wendiceratops is the oldest known horned dinosaur to have a big nose horn, so it’s nice to help us figure out when and how that classic skull feature evolved,” he said in an email interview. “Most interestingly, it adds to a body of evidence that shows big nose horns evolved at least twice in horned dinosaurs. Again and again, distantly related species of these dinosaurs converged on similar anatomy.”
The other revelation was the sheer number of fossils found at this bone bed. There are signs that scores of Wendiceratops died here, possibly from a flood or some other natural catastrophe. Today, it’s a remote stretch of badlands but, in the day of Wendiceratops, it would have been a low-lying coastal plain that looked more like Louisiana.
“There is no sign of deposits running out so there could be dozens of individuals in the bone bed,” Evans said. “It actually reinforces that Wendiceratops was a social animal. We have evidence these animals died together so it’s likely therefore they were living together as part of a herd when they were struck by a catastrophe such as a flood.”